Marketing Management Fundamentals
Understanding the Core Principles, Strategies, and Ethical Considerations in Modern Marketing
Marketing management is a critical function within any organisation, bridging the gap between a company’s products or services and its target audience. It encompasses strategic planning, market research, branding, pricing, promotion, and distribution. Rooted in both art and science, effective marketing management requires analytical rigour, creative problem-solving, and a deep understanding of consumer behaviour.
Philip Kotler, often regarded as the father of modern marketing, defines marketing management as
“The analysis, planning, implementation, and control of programs designed to create, build, and maintain beneficial exchanges with target buyers for the purpose of achieving organisational objectives.”
This definition underscores the strategic and results-driven nature of marketing management. With this quote ringing in our ears, let’s dive into the core principles of Marketing Management…
The Marketing Made Clear Podcast
This article features content from the Marketing Made Clear Podcast – check it out on all good platforms.
The Core Principles of Marketing Management
1. Market Orientation and Customer Focus
A successful marketing strategy begins with a customer-centric approach. Market orientation involves understanding consumer needs, preferences, and behaviours to develop products and services that deliver value. Organisations that prioritise customer satisfaction foster long-term relationships and achieve sustainable growth.
Kotler’s concept of the marketing concept highlights that organisations should identify and satisfy customer needs better than competitors. This principle shifts the focus from selling what a company produces to producing what the market demands.
2. Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP)
One of the most fundamental frameworks in marketing management is the STP model:
-
Segmentation: Dividing a heterogeneous market into smaller, more manageable segments based on demographics, psychographics, geographic location, or behavioural factors.
-
Targeting: Selecting the most viable segments to focus on based on factors such as profitability, size, and accessibility.
-
Positioning: Crafting a distinct brand image and value proposition that differentiates the product in the minds of consumers.
This framework ensures that marketing efforts are efficient and aligned with the most receptive audience.
3. The 7Ps of Marketing (Extended Marketing Mix)
The traditional marketing mix, conceptualised by Jerome McCarthy and popularised by Kotler, consists of four key elements:
- Product: The goods or services offered to meet customer needs.
- Price: The monetary value assigned to the product, influenced by market demand, competition, and perceived value.
- Place: The distribution strategy to ensure the product reaches the right customers at the right time.
- Promotion: The communication strategy, including advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and digital marketing, to engage and persuade consumers.
In the modern marketing landscape, three additional elements have been incorporated to better address service-oriented businesses, becoming the 7P’s of Marketing:
- People: The individuals involved in delivering the product or service, including customer service teams and brand representatives.
- Process: The systems and procedures that ensure efficient service delivery and customer experience.
- Physical Evidence: Tangible elements that reinforce the brand’s presence, such as packaging, store layout, and website aesthetics.
- Promotion: The communication strategy, including advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and digital marketing, to engage and persuade consumers.
Read more about the 7P’s of Marketing here.
4. Brand Management and Positioning
Branding is a cornerstone of marketing management, influencing consumer perception, loyalty, and competitive advantage. A strong brand is built on consistent messaging, visual identity, and emotional connections with customers.
Positioning strategies, such as differentiation (offering unique value) and cost leadership (competing on price), dictate how a brand is perceived in the market. Effective brand management ensures long-term equity and sustained competitive advantage.
5. Consumer Behaviour and Psychology
Understanding consumer decision-making processes is essential for developing impactful marketing strategies. Psychological factors, such as perception, motivation, attitudes, and cultural influences, shape purchasing behaviour. Marketers leverage insights from behavioural economics and cognitive psychology to craft persuasive campaigns.
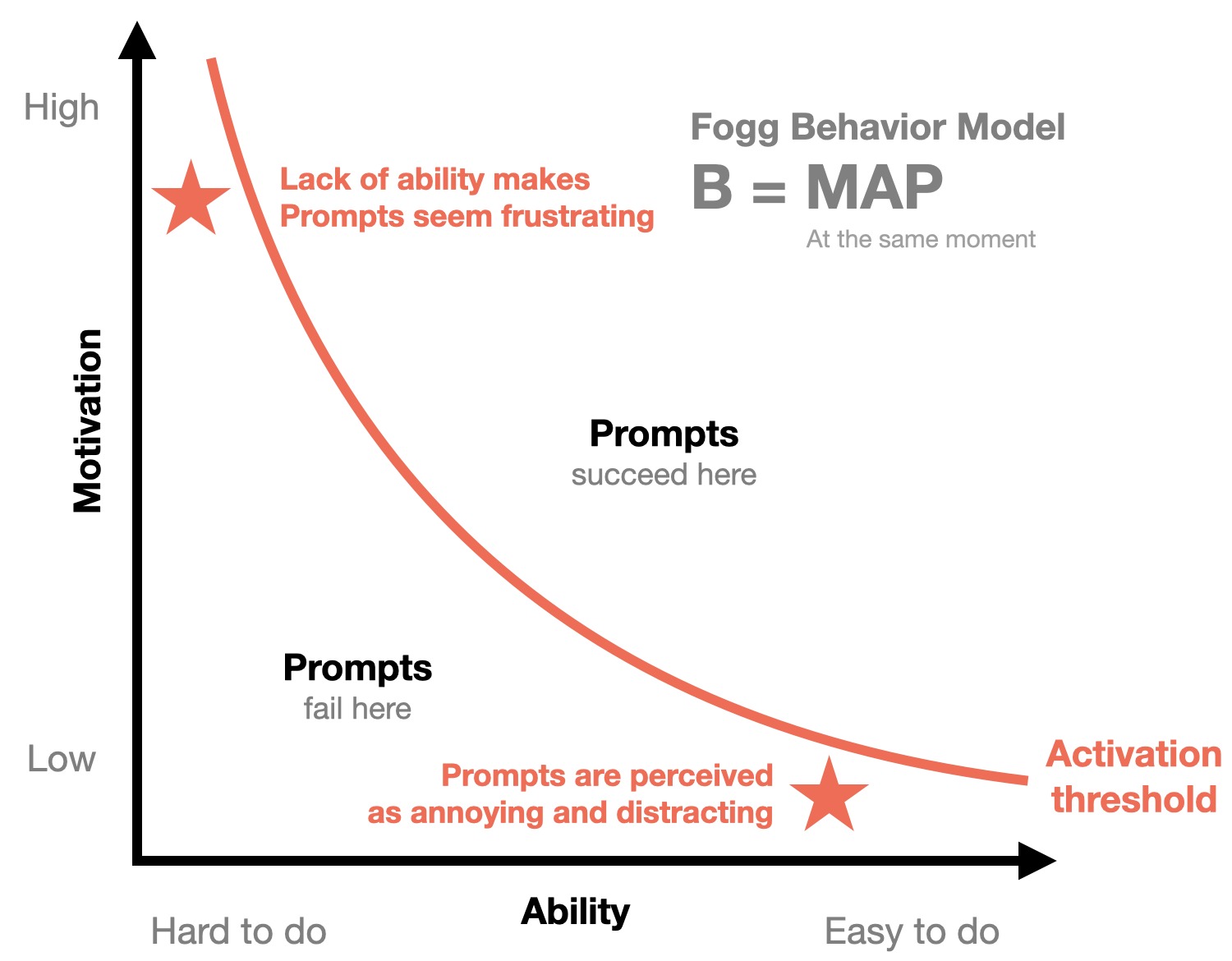
For instance, the Fogg Behaviour Model explains that consumer action is influenced by three factors: Motivation, Ability, and Triggers. Marketers must align their messaging with these factors to drive conversions and engagement.

Strategic Marketing Planning and Execution
6. Marketing Strategy Development
A robust marketing strategy aligns with an organisation’s overall business objectives and includes:
-
Situation Analysis (SWOT, PESTEL) to assess internal and external factors.
-
Goal Setting using SMART objectives (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
-
Tactical Implementation via integrated marketing communications (IMC) across multiple channels.
7. Digital Marketing and Data Analytics
With the rise of digital platforms, marketing management has become increasingly data-driven. Marketers utilise SEO, content marketing, social media, and paid advertising to reach and engage audiences. Analytics tools, such as Google Analytics and CRM systems, provide actionable insights into customer behaviour and campaign performance.
8. Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Marketing managers must track performance metrics to evaluate campaign effectiveness. Common KPIs include:
-
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
-
Return on Investment (ROI)
-
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
-
Conversion Rates
-
Engagement Metrics (CTR, Bounce Rate, Social Shares)
Data-driven decision-making ensures continuous optimisation and refinement of marketing strategies.
Ethical Considerations in Marketing Management
In the era of transparency and accountability, ethical marketing practices are non-negotiable. Orwellian deceptive tactics, such as misleading advertising or data exploitation, damage brand reputation and consumer trust. Marketers must adhere to principles of honesty, fairness, and social responsibility, ensuring that marketing strategies align with ethical standards and regulatory guidelines.
Conclusion
Marketing management is an ever-evolving discipline that blends strategy, creativity, and analytics. By mastering the fundamentals – customer focus, segmentation, branding, digital marketing, and ethical practices – marketers can drive business success and create lasting consumer relationships.
As Kotler emphasised,
“Marketing is not the art of finding clever ways to dispose of what you make. It is the art of creating genuine customer value.”
Understanding and applying these fundamentals will equip marketing professionals with the tools to thrive in an increasingly competitive and dynamic marketplace.


